Good Morning,
Stocks rose to record levels on Friday, notching another weekly advance, as investors shook off a disappointing U.S. jobs report.
Friday’s jump led major averages to their fourth weekly gain in five weeks. The Dow rose 1% this week. The S&P 500 gained 1.7% over that time period. The Nasdaq Composite rallied 2.2% this week.
The U.S. economy added 245,000 jobs in November. That’s well below a Dow Jones consensus estimate of 440,000. The unemployment rate, however, matched expectations by falling to 6.7% from 6.9%.
However, investors took the “bad news is good news” approach viewing the weaker-than-expected number as a positive as it could pressure lawmakers to move forward with additional fiscal stimulus.
Our Take
November is in the books, recording one of the best months in market history. That makes it six out of the last eight months where the S&P has recorded gains since the March lows. More importantly, all of the major indices showed strength reaching new all-time highs in unison. Based on historical patterns, while there is usually a period of "'give back" following such an event, this kind of market breadth typically foreshadows continued equity market gains…
Although there were some concerning data points in Friday’s jobs report data, Chris Williamson, Chief Business Economist at IHS Markit noted that:
"November saw US business activity surge higher at a rate not seen since early-2015 as companies enjoyed sharply rising demand for goods and services. Confidence has picked up considerably, with encouraging news on vaccines coinciding with reduced political uncertainty following the presidential election, hopes of greater stimulus spending, and fresh stock market highs. Optimism about the future is running at its highest since early 2014.The recent improvement in demand and the brightening outlook encouraged firms to take on extra staff at a rate not previously seen since the survey began in 2009, underscoring how increased optimism is fuelling investment and expansion. Pricing power is also being regained, with firms pushing up average charges for goods and services at a rate not seen for at least a decade, boding well for stronger profits growth."
Furthermore, despite the continued negativity regarding how the U.S. is responding to the virus, it finds itself leading the global recovery. In aggregate, Markit data show the U.S. economy accelerating rapidly, with November being the best month since September of 2014 for manufacturing's growth rate, the best month since March of 2015 for services' growth rate, and the best month since March of 2015 for the output-weighted composite of these two indicators.
Globally, Europe appears to be flirting with a double dip recession yet China and Japan as the world’s second and third largest economies, are currently helping keep the global expansion on track. Asian strength bodes well for a global recovery to take shape once COVID is less of an issue. Price action is confirming that view. Asia-Pacific equity markets have broken out to the upside. Japan, Korea, Taiwan, and India are all at decade-plus or all-time highs, while other markets have participated as well. A synchronized global recovery is underway.
South Korea now leads this part of the globe in gains for Industrial production, a 10-year yield of 0.24%, and their Stock Market (KOSPI) is nearing an all-time high.
In aggregate, these economies are growing faster with lower rates than the rest of the world average, a positive backdrop for further equity market gains.
But what of the growing bullishness among individual investors with sentiment reaching highs?
AAII sentiment survey for this week shows the Bulls in the majority at 49%, a slight increase over last week. Other sentiment surveys are echoing the exuberance among investors. The Investors Intelligence survey of equity newsletter writers likewise saw bullish sentiment rise again this week from what were already strong levels. 64.7% of respondents reported as bullish this week. That is in the top 3% of all readings in the history of the survey. The last time this reading on bullish sentiment was this elevated was in January of 2018.
In addition, CNN’s Fear and Greed Index hit over 90 in November and is hovering above 80. What a contrast to March lows…
Fund managers are the most optimistic on the stock market and economy that they’ve been all year, according to Bank of America’s fund manager survey.
Are prices getting ahead of themselves? Have we entered into another bubble? Is this the top? Equity markets, bitcoin, housing, gold, copper etc. The list of assets at or at least close to all time highs goes on.
I must say that this month we’ve had more people than ever before reach out to us and ask about how to get into the equity markets. The above, in addition to the rising chorus of Twitter investors (Fintwit) becoming more and more vocal about their returns, more brazen in their attitude towards value and price:
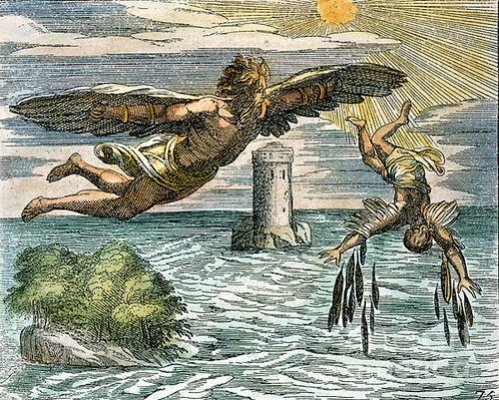
Has caused us to yet again dust off and reflect upon one of our favourite myths. The myth of Icarus.
Musings
In Greek mythology, Icarus was the son of the master craftsman Daedalus, the creator of the Labyrinth. Icarus and his father attempted to escape from Crete by means of wings that Daedalus constructed from feathers and wax. Icarus' father warns him first of complacency and then of hubris, asking that he fly neither too low nor too high, so the sea's dampness would not clog his wings nor the sun's heat melt them. Icarus ignored his father's instructions not to fly too close to the sun; when the wax in his wings melts he tumbles out of the sky and falls into the sea where he drowns, sparking the idiom "don't fly too close to the sun".
This is a stark illustration of the tragic theme of failure at the hands of hubris. Hubris being a personality quality of extreme or foolish pride or dangerous overconfidence, often in combination with (or synonymous with) arrogance.
We’ve always liked this story as its imagery is easy to remember as fear turns to greed and begins to cloud the mind and influencing judgement. The story is timeless and so is the outcome. Markets are still at their core a story of human emotion.
Why does the myth of Icarus matter today?
Sentiment is no doubt becoming extended. Yet by and large we do not feel it is helpful to think of what is going on as a “bubble”.
A better way to think about the current environment is in terms of “cycles” rather than “bubbles”.
In an article written back in 2016 by Morgan Housel, he reminds us “that most of what people call a bubble turns out to be something far less sinister: A regular cycle of capitalism.”
Cycles are one of the most fundamental and normal parts of how markets work and are rooted in human emotion. They look like this:
“This cycle is self-reinforcing, because if assets didn’t get expensive they’d offer big returns, and offering big returns attracts capital, which makes them expensive. That’s why cycles are everywhere and we can never get rid of them.”
“A bubble in contrast is when this cycle breaks. It’s only a bubble if return prospects don’t improve after prices fall. It’s when an asset class offers you no hope of recovery, ever. This only happens when the entire premise of an investment goes up in smoke.”
“That was true of a lot of dot-com stocks, which weren’t bargains after they fell 90% because there was still no tangible company backing them up. It was true of homes in the mid-2000s, because you stood no chance of enjoying a recovery if you were foreclosed on. It was true of Holland’s 1600s tulip bubble, as the entire idea that tulips had any value went up in smoke.
But it wasn’t true of stocks in 2007. Yes, the market fell 50%. But that made it so cheap – particularly compared to the alternative of bonds – that buyers instantly came rushing back in. Prices hit a new all-time high by 2013.”
Fast forward to the COVID-19 induced melt-down in March. Many businesses that have since recovered weren’t broken, and valuations had in many cases never been cheaper after the crash. It should not be surprising then that many have bounced back so aggressively as their low prices offered large returns.
Bubbles should be avoided, because they present the prospect of permanent capital loss. If on the other hand you find assets that look overbought and expensive (perhaps those hitting ATHs outlined above) the chances that they will fall may be elevated yet you likely haven’t encountered a bubble. You’ve instead found capitalism. Excesses will correct, the business will chug on and the humble investor will patiently make a return. Life goes on in a surprisingly predictable way:
Furthermore, when it comes to the first year of a presidential term, the odds of a rising market are 82%, versus 70% in the other three years of the term. But even this difference is not significant at the 95% confidence level that statisticians typically use to determine if a pattern is genuine.
Despite the above probabilities that the market will end positive at the end of each time period, just about every year since 1926 there have been “experts” predicting market “mayhem”, “collapses” or “crashes”.
Whether an individual expert is wrong or right in their call isn’t the point. The point is that these cycles are inevitable.
Just as in our own lives, as we were so brutally reminded over the last 10 months of COVID-19, we can’t spot the end or the beginning of these inevitable ups and downs or cycles with great precision. That’s what we signed up for as a human and as an investor.
Instead, all we can do is remain alive to their existence and attempt to play the ball as it lies. The story of Icarus, which is also inevitably destined to repeat itself, can help us do so.
Where are we now?
Based on the data, there is a greater than average probability that we are transitioning out of the “People rush in to exploit opportunity” phase to the “Prices are bid up” phase. Icarus is likely flying closer and closer to the sun.
Central banks and governments have succeeded in putting together an extremely favourable backdrop for “risk-taking” and thus “asset price-inflation”. Investors are thus being rewarded for taking on risk.
When investors take 'a little risk' and get rewarded for it, they are then encouraged to take 'a little more risk.' Investors in the 'crowd' don't appreciate the risks they are taking because they're surrounded by people who believe the market will keep going up.
Such appears to currently be the case. Many are thoroughly convinced that markets cannot go down due to the Federal Reserve and government interventions.
Without arguing for or against the wisdom of this belief, we can instead simply view it as a feature of this current market. While future long-term returns based on today’s prices are obviously lower than if one were first investing capital during the March crash, that does not necessarily mean long-term returns will be negative.
Just because current opportunities may not be as attractive as 9 months ago does not mean sitting on cash to wait for the next correction is the best decision. While there is risk that the market may decline in the future, historically (as shown by the data above) there is MORE risk that it will go up.
As such, we believe at this point in the cycle caution through active portfolio risk management and a renewed focus on company specific stock selection rather than simply sector/index exposure is warranted.
Charts of the Month
Cycles in perspective.
One method of evaluating the S&P 500 (SPX) is to subtract the six-month Treasury yield from the SPX dividend yield to get the "net yield". By this measure, stocks are historically cheap. Further, the profile of the net yield is similar to 1995 and 1998, just before two explosive, multi-year rallies in the SPX. Could a new technological revolution be taking hold which will send the stock market to levels that few people can imagine...just like in the late 1990s?
Reduced deficit spending always precedes recessionary periods (red outlines below). Throughout the 1990s, Clinton reduced the deficit and finally eliminated it, sending the budget into surplus.
Logos LP November 2020 Performance
November 2020 Return: 25.71%
2020 YTD (November) Return: 89.34%
Trailing Twelve Month Return: 89.38%
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) since inception March 26, 2014: +24.79%
Thought of the Month
"Amor fati, for Nietzsche, meant the unconditional acceptance of all life and experience: the highs and the lows, the meaning and the meaninglessness. It meant loving one’s pain, embracing one’s suffering.” -Mark Manson
Articles and Ideas of Interest
How do we prevent the next outbreak? Vaccines are on the way. There appears to be light at the end of the tunnel. But we are still, for the most part, shut down as we wait for vaccines to be rolled out. Our governments have chosen a virus containment approach consisting of rolling draconian lockdowns which have and will continue to cause permanent economic and social damage. This doesn't seem to be a sustainable long-term approach and sets a problematic precedent. What if COVID-19 was not a "black swan" but instead just the first of many in a new era of deadly global pandemics? What if, not long after the vaccine roll out, we are hit with the next global pandemic? Will citizens expect their governments to again attempt to protect every last human life by demanding another round of massive economic and social sacrifices until a vaccine is developed? Are politicians even considering such a new era of frequent deadly pandemics? Coronaviruses, like the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, are not uncommon. The WHO estimates that some 60 percent of all viruses that infect humans come from animals. This phenomenon is termed “zoonosis.” The WHO finds that 75 percent of new infectious diseases in the past decade are zoonotic. Our planning needs to take into account the complex interconnections among species, ecosystems and human society. The Scientific American digs in and explores what we can do to prevent infection by the next emerging virus.
Blackrock’s Chief Investment Officer says Bitcoin could replace gold to a large extent. The chief decision maker for where BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, invests its funds said bitcoin could take the place of gold to a large extent because crypto is “so much more functional than passing a bar of gold around.” What would the implications of this shift be on the roughly $9 trillion dollar market capitalization of gold and those who hold it? In the meantime, US investors who variously view the virtual currency as a “risk-on” asset, a hedge against inflation and a payment method gaining mainstream acceptance are gobbling up the asset.
Major scientific advance: DeepMind AI AlphaFold solves 50-year-old grand challenge of protein structure prediction. In a major scientific advance, the latest version of DeepMind’s AI system AlphaFold has been recognized as a solution to the 50-year-old grand challenge of protein structure prediction, often referred to as the ‘protein folding problem’, according to a rigorous independent assessment. This breakthrough could significantly accelerate biological research over the long term, unlocking new possibilities in disease understanding and drug discovery among other fields.
Why value stocks won’t necessarily keep outperforming growth. A fading of the economy’s momentum would favor growth stocks over value, contrary to the recent trend. A decline in expectations for inflation would mean a less upbeat outlook for economic growth, and for corporate profits.
Boom times have returned for venture-backed start-ups, says co-founder of $3 billion fintech Brex that lends to thousands of other start-ups. Customer spending is now at an all-time high, roughly 5% higher than it was before the pandemic, he said, but companies are transacting differently than they used to, plowing dollars into online advertising and remote work expenses. New companies are being formed at a furious clip, Dubugras says, and many of these firms – retailers, restaurants or professional services— are “looking more and more like tech companies.”
The new casino. Pandemic-induced options trading craze shows no signs of slowing down. The stay-at-home requirement created by Covid-19 has spawned a huge sub-industry in options trading in tandem with an increase in equities trading that shows no signs of letting up. Trading in equity options hit new highs in November, continuing a trend that began earlier in the year. Equity option trading is 50% above last year’s levels year to date on all the options platforms. Human nature is undefeated…
Prepare your portfolio for a return of the roaring 20s. Some naysayers point to surveys suggesting that consumers plan to maintain the savings habit once lockdown is over. But after a year of no holidays, no eating out and no high street shopping sprees, how inclined to fiscal prudence will we really feel? We suspect this is one of the few occasions where the phrase “pent-up demand” has genuine meaning. So the stage is set for a short-term boom as all that delayed demand floods out in the early part of next year. But what happens then? Why will this be anything more than a short-term sugar rush? MoneyWeek makes the uber bull case...
How Covid-19 will change aging and retirement. As the pandemic wreaks havoc on our mental and physical health, it is also quietly reshaping how Americans will face retirement and old age in the years to come. It will make people rethink retirement altogether as well as fuel a boom in innovation improving life in later years. Interesting piece in the WSJ exploring the themes above.
After Covid, “Normal” could be profoundly different. Those expecting things to go “back to normal” after ten months of new habit building maybe in for a surprise. Even when lockdowns are a thing of the past, we’ll be spreading out in the suburbs and ordering in. The economy may never be the same. Any of these changes on their own could well have redirected tens or hundreds of billions of dollars in government and consumer spending from one place to another, but they are all happening at the same time. Some of the trillions of dollars’ worth of aircraft, cruise ships, gyms, shopping malls, office buildings, hotels and convention halls have been sitting idle may not be needed even after it is safe to use them. Others like e-commerce infrastructure can’t be built fast enough. The WSJ digs in.
How companies like Nike and Apple stay cool for decades. Very few brands manage to navigate coolness alongside an extreme rise in popularity, and two have done it more successfully than anyone else: Nike and Apple. Both maintain their credibility by preserving some of what originally earned them acolytes, while constantly tinkering with new ideas to stay relevant. Here’s how these two titans have kept their edge for decades, and what other companies might learn from them.
All successful relationships are successful for the same reasons. 1,500 People give all the relationship advice you’ll ever need. Mark Manson reached out to those who have been married for 10+ years, and is still happy in their relationship and asked what lessons would you pass down to others if you could? What is working for you and your partner? Also, to people who are divorced, what didn’t work previously? The response was overwhelming. What he found was incredibly repetitive. The same twelve things are here.
Our best wishes for a Holiday filled with joy and contentment,
Logos LP